|
Research programme
Corrosion protection In the field of corrosion protection our research is focused on the following topics:
Corrosion Inhibitors The inhibition of corrosion using corrosion inhibitors has been for decades one of the most important method of corrosion protection. Inhibitors are inorganic or organic compounds which when added in small concentrations form a surface layer that protects the underlying metal surface from dissolution and, consequently, decreases the corrosion rate. The choice of inhibitors is based on its inhibition efficiency but also on price and environmental harmlessness. Our research studies are focused on liquid-based inhibitors. These can be classified as anodic, cathodic and mixed depending on whether they mainly affect anodic, cathodic or both reactions, respectively. Mixed inhibitors affect both anodic and cathodic reaction and can act through physisorption, chemisorption and film formation. Among the most important inhibitors for copper are triazole and imidazole-based inhibitors. Benzotriazole (BTAH) has been known since 1947 to be a very effective inhibitor of corrosion for copper and copper alloys. A number of inhibitors was investigated in our laboratory, mainly for copper-, zinc- and iron-based metals. Modelling based on density functional theory (DFT) became indispensable help when explaining experimental observations. It provides data on adsorption mechanism and bonding of inhibitors on the metal surface. Additionally it allows for the calculations of electronic properties of the metal/adsorbate system, which can provide physical insight into the processes of corrosion and corrosion inhibition. One of the recent trends in corrosion protection is the synergistic use of inhibitors. The combination of different inhibitors can either increase the effect of each inhibitor individually, or bring additional functional property, for examples hydrophobicity.
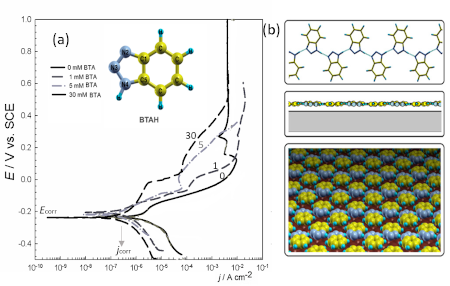
Figure: (a) Polarization curves recorded for copper in 0.5 M NaCl with and without benzotriazole (BTA) added in concentration of 1, 5 and 30 mM. Scan rate was 1 mV/s. (Reprinted from the publication by T. Kosec, I. Milošev, B. Pihlar, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2007, 253, 8863–8873) Skeletal structure of BTA is given in inset. (b) The structure of BTA is planar and therefore favourable for physisorption on metal surface as shown by tentative structure; planar physisorbed BTAH polymers are packed so as to form compact and thin film. (Reprinted from the publication by M. Finšgar, A. Lesar, A. Kokalj, I. Milošev, Electrochim. Acta, 2008, 53, 8287–8297)
Projects related to corrosion inhibitors
|